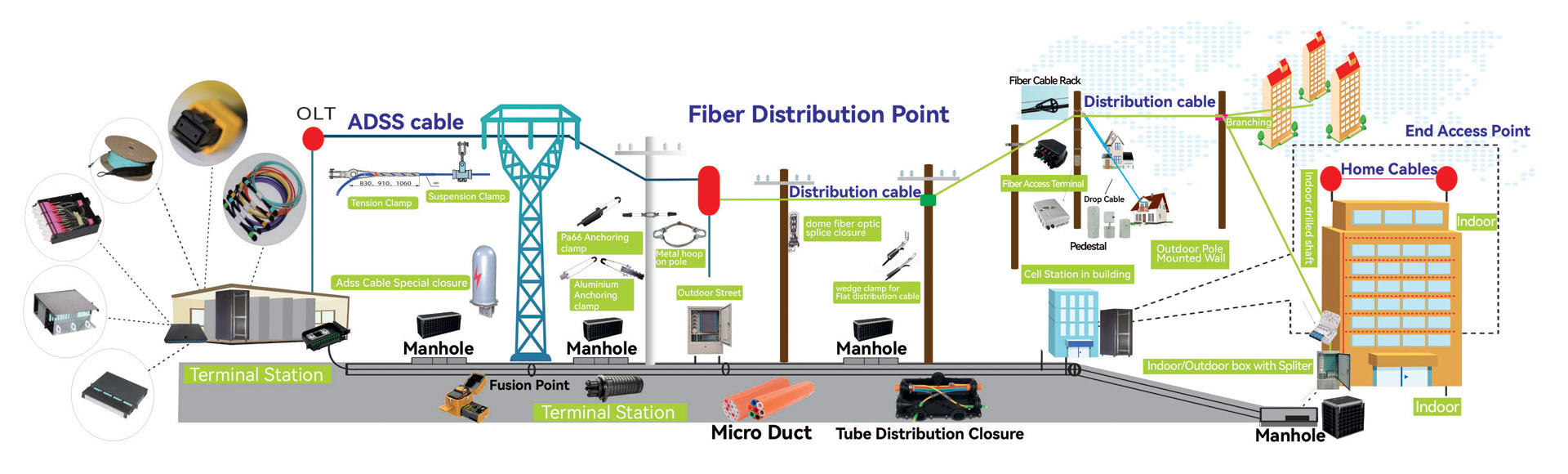
Due to external factors or the optical fiber itself and other reasons caused by the block of the cable line affecting the communication service is called the cable line fault. Service interruption is not always caused by cable interruption. If a fault causes service interruption, handle it according to the fault repair program. If no fault occurs, handle it according to the cutover program.

1 Classification of optical cable faults
According to the optical fiber blocking of the faulty cable, the fault can be divided into three types: complete cable break, partial beam tube break, and partial optical fiber break in the single beam tube.
1.1 The optical cable is completely broken
If there are reservations on both sides of the site, the method of centralized reservation and adding a joint is adopted.
If there is a joint near the fault point and there is enough reservation on site, pull the reservation and use the original joint.
If there is neither reservation nor connector near the fault point, it is advisable to use a follow-up cable.
1.2 Part of the beam tube in the optical cable is interrupted or part of the optical fiber in the single beam tube is interrupted
The optical fiber in use is not affected. You are advised to use the skylight connection method to repair the faulty optical fiber.
picture
2 Cause analysis of optical cable line fault
The causes of cable line failure can be roughly divided into four categories: external factors, natural disasters, optical cable defects and human factors.
2.1 Line faults caused by external factors
(1) External force mining: processing excavator construction digging fault, pipeline cable due to open the fault point near the manual well to see whether the cable is damaged in the manual well, and two-way test interrupted cable (2) vehicle hanging up: when dealing with the car hanging fault, should first fault point cable for both sides to test, confirm the number of cable blocking, and then targeted processing.
(3) Shooting: This kind of fault generally will not interrupt all optical fibers, but some parts of the cable or optical fiber damage, but this kind of fault is difficult to find.
2.2 Line faults caused by natural disasters
Rat bites and bird pecks, fire, flood, wind, ice, lightning strikes, electric shocks
picture
2.3 Line Faults caused by optical fibers
(1) Natural fiber breaking: As the fiber is made of glass and plastic fibers, it is relatively fragile. With the passage of time, static fatigue will occur, and the gradual aging of the fiber will lead to natural fiber breaking. Or the connector box is flooded, resulting in increased optical fiber loss, or even fiber breakage.
(2) The influence of ambient temperature: too low temperature will lead to ice of water in the joint box, longitudinal shrinkage of the cable sheath, pressure on the fiber to produce slight bending, which will increase the attenuation or interrupt the fiber. The temperature is too high, and easy to make the cable sheath and other protective material damage affect the fiber characteristics.
2.4 Line faults caused by human factors
(1) Work obstacles: artificial faults caused by technicians during maintenance, installation and other activities. For example, when connecting the optical fiber, the optical fiber is scratched and the bending radius of the optical fiber is too small. Mistakenly cutting the cable while it is in operation; The fiber is broken because the fiber is not properly connected or the core is not tightly fixed when the connector box is packed.
(2) Theft: criminals steal and cut optical cable, resulting in optical cable blocking.
(3) Damage: human deliberate damage, resulting in cable blocking.
3 Troubleshooting principles
For the purpose of giving priority to the in-use system, and based on the compression of failure duration, the fastest way is used to temporarily rush the in-use transmission system regardless of day and night, regardless of weather or maintenance boundaries.
The general principles for troubleshooting are as follows: First connect, then repair; Core first, edge after; First local end, then peer end; The fault should be handled by fault level in the network first and then out of the network. If more than two faults occur at the same time, handle major faults first. The inspection and repair shall not be suspended before the obstacles are removed.
picture
4 Make emergency scheduling plans for lines
Before formulating the emergency dispatching plan, the system opening situation of all optical cable lines should be carefully investigated, and according to the situation of optical fiber resources of the same cable and the same route, the optical fiber scrambling plan should be reasonably formulated.
The emergency Jiedaitong plan should be timely revised and updated according to the circuit opening and fiber core occupation, so as to keep the plan consistent with the actual opening situation and ensure the feasibility of the emergency plan.
The content of the emergency dispatching plan shall include the personnel involved, the leading organization, the concrete measures and the detailed circuit dispatching plan.
picture
5 Process for repairing Optical cable faults
1. Handle faults after they occur. Different types of line faults have different priorities.
(1) The same route has a cable can be replaced by a total resistance fault. According to the emergency plan, the personnel on duty in the equipment room should use other good core core-communication devices to block the services on the optical fiber and then repair the faulty optical fiber as soon as possible.
(2) If there is no total resistance fault that can be replaced by optical fiber, the emergency plan shall be carried out in accordance with the direct repair of the switching or obstacle points. The principle of "important circuit first, then minor circuit" shall be followed during the switching or repair.
(3) The optical cable appears incomplete resistance, and there are residual optical fibers available. Use a spare fiber core or other fiber optic cable on the same route to replace the service on the faulty fiber core. If the fault core is more, spare fiber core is not enough, and there is no other same route cable, can sacrifice the secondary circuit through the important circuit, and then use the method of non-interruption circuit to repair the fault core.
(4) The optical cable appears incomplete resistance, no remaining optical fiber or the same route optical fiber. If the blocked fiber is an important circuit, use other non-important circuit fiber pass-through to block the fiber, and use the method of uninterrupted cutover to repair the faulty fiber core.
(5) Transmission quality is not stable, the system is good and bad. If there is a spare fiber core or other optical fiber that is the same route, you can switch the service on the optical fiber to another optical fiber. Find out the reason of transmission quality degradation and deal with it accordingly.
2. Locate the fault
If an optical cable is faulty, quickly determine the trunk segment in which the fault occurs and the specific fault information, and consult the network management equipment room for details. According to the judgment result, the relevant line maintenance unit should be notified immediately to detect the fault point.
3. Prepare for rush repair
After receiving the fault notice, the line maintenance unit shall promptly load and set off the emergency repair tools, instruments and equipment, and notify the relevant maintenance lineman to find the cause and fault point in the nearby area. The preparation time for rush repair of optical cable lines shall be carried out in accordance with regulations.
4. Establish a communication system
After arriving at the fault point, the emergency repair personnel should establish a communication system with the transmission room immediately.
5. Responsible for the organization and command of emergency repair
The emergency repair of optical cable line fault by the maintenance department as the business leadership, during the emergency repair to pay close attention to the situation of the scene, do a good job with the work, the emergency repair site by the leadership of the optical cable line maintenance unit as the command.
At the same time of testing the fault point, a special person (usually a cable operator) should be designated at the site to organize excavation personnel to be on standby and arrange logistics services.
6, cable line repair
When the fault is located, use emergency optical cables or other emergency measures to connect the main fiber channel to quickly restore communication. Observe and analyze the situation at the scene, make records, take photos and report to the public security organs.
7. Services are restored
After the onsite cable repair is completed, inform the equipment room for testing in time, verify that the cable is available, and resume communication as soon as possible.
8. On-site treatment after rush repair. After the rush repair work, check the tools and equipment, sort out the test data, fill in the relevant registration, process the site, and leave a certain number of personnel behind to protect the site of Bandaitong.
9. Update of line information. After the repair work, sort out the test data, fill in the relevant forms, update the line information in time, summarize the emergency repair situation, and report to the superior department.
6 Common faults and possible causes
picture
1. Distance judgment
When the machine room determines that the fault is the fault of the optical cable line, the line maintenance department should test the faulty optical cable line in the machine room as soon as possible, and determine the location of the fault point of the line with OTDR test.
2. Possible cause estimation
According to the curve displayed by OTDR test, the cause of the fault is determined preliminarily and the fault is dealt with accordingly.
According to the fault analysis, there are more problems in the connector box than in the cable failure caused by external forces. The causes of fiber breaking or attenuation increase in the connector box can be divided into the following situations:
(1) The optical fibers in the fiber tray are loose, causing the optical fibers to spring up on the edge of the fiber tray or the screws on the tray to be squeezed. In serious cases, the optical fibers will be crushed or broken.
(2) The local bending radius of the residual fiber in the joint box is too small or the fiber is twisted seriously when the disc is put in storage, resulting in large bending loss and static fatigue. The change is not obvious at 1310nm wavelength test, and the joint loss increases significantly at 1550nm wavelength test.
(3) When making optical fiber end face, the bare optical fiber is too long or the optical fiber protection position is improper when the heat shrink protective tube is heated, resulting in a part of the bare optical fiber outside the protective tube, and the bare optical fiber will break when the external force is applied to the joint box.
(4) When stripping the coating layer, the bare fiber is injured. After a long time, the damage expands, the joint loss increases, and in serious cases, the fiber is broken.
(5) Because the cable fixed is not tight, the cable due to the effect of stress or external force displacement resulting in fiber optic fiber distortion or bending changes caused by fiber attenuation.
(6) Water into the connector box, freezing in winter leads to increased optical fiber loss, and even fiber breaking.
3, find the specific location of the fault point of the cable line
When encountered natural disasters or external construction and other obvious external force caused by the cable line block, check and repair personnel according to the test personnel to provide fault phenomena and approximate fault location, along the cable route carefully patrol, generally easier to find the fault location. Otherwise, the inspector will not easily find the fault location from the routing anomaly. At this time, it is necessary to check with the original test data according to the distance between the fault point and the test end measured by OTDR to find out which two markers (or which two joints) the fault point is between, and find the specific location of the fault point after the necessary conversion. If possible, two-way testing can be carried out to determine the exact location of the fault point.
4, the main reasons affecting the accurate judgment of cable line obstacle points
(1) OTDR has inherent deviation
The inherent deviation of OTDR is mainly reflected in the range resolution. Different test range deviation is different. When the test range is 150km, the test error is up to ±40m.
(2) Error caused by improper operation of test instrument
The correctness of OTDR is directly related to the accuracy of the obstacle test when testing cable fault location. For example, improper setting of instrument parameters or inaccurate setting of vernier will lead to error of test results.
(3) Calculation error
OTDR measured fault point distance can only be the length of the optical fiber, can not directly get the cable length and test point to the obstacle point of the ground distance, must be obtained through calculation, and in the calculation because the value can not be completely consistent with the actual or the use of the cable shrinkage rate is not clear, will also produce a certain error.
(4) Error caused by inaccurate completion data of optical cable lines
Due to the lack of attention to the accumulation of data during the construction of the line or the low credibility of the recorded data, the completion data of the line is inconsistent with the reality, based on such data, it is impossible to accurately determine the obstacle points.
For example, when the cable is connected, the length of the remaining fiber in the joint box, the length of the cable at various special points and the cable changes with the relief of the terrain, the accuracy of these factors directly affects the positioning accuracy of the obstacle points.
5, improve the accuracy of optical cable line fault location method
(1) Correct and proficient in the use of instruments
Accurately set the parameters of OTDR, select the appropriate test range file, apply the instrument amplification function, and accurately place the vernier on the corresponding inflection point, such as the inflection point of the fault point, the beginning point of the fiber and the end point of the fiber, so that more accurate test results can be obtained.
(2) Establish accurate and complete original data
Accurate and complete optical cable data is the basic basis of obstacle measurement and judgment. Therefore, it is necessary to attach importance to the collection, collation and verification of line data, so as to establish a real, credible and complete line data.
(3) Establish accurate route data, including the comparison table of marker (rod number) -- Length (cable length) (refer to the appendix), record of "Optical fiber Length accumulation" and "Optical fiber decay". When establishing "Optical fiber length accumulation" data, the distance between terminal station and each connector should be measured from both ends respectively. In order to achieve accurate test results, transitional optical fibers can be used as required. The inspection and acceptance personnel collect and record various reservation lengths. The more carefully registered, the smaller the error of obstacle determination.
(4) Establish complete and accurate line data
The establishment of line data not only includes many data in line construction, completion technical documents, drawings, test records and relay section of optical fiber backscattered signal curve pictures, etc., but also should retain some original data of optical fiber and optical fiber provided by the manufacturer when the cable factory (such as optical fiber shrinkage rate, refractive index of optical fiber, etc.), these data is the foundation and comparison basis of obstacle test in the future.
(5) Make the correct conversion
To accurately determine the location of the fault point, the length of the optical fiber tested must be converted to the length of the ground from the test end (or a joint point) to the fault point.
The ground length from the test end to the fault point can be calculated by the following formula (length unit is m) :
L = [(L1-L2)/(1+P)-L3]/( 1+a )
Where, L is the ground length from the test end to the fault point (unit: m); L1 is the optical fiber length measured by OTDR from the test end to the fault point (unit: m); L2 is the optical fiber length left in the disc of each joint box (unit: m); L3 is the optical cable and all disc lengths at each joint (unit: m). P is the twisting rate of optical fiber in the cable (i.e. twisting coefficient), it is best to apply the value provided by the manufacturer, generally 7‰, a is the cable natural bending rate (pipe laying or overhead laying can be 0.5%, directly buried laying can be 0.7%-1%). With accurate and complete original data, the fault fiber length measured by OTDR can be compared with the original data, and the location of the fault point can be accurately identified.
(6) Keep the consistency of obstacle test and test conditions on the data
During fault testing, the signal, operation method and parameter Settings of the test instrument should be consistent as far as possible. Because the optical instrument is very precise, if there is any difference, it will directly affect the accuracy of the test, resulting in the difference between the two tests itself, so that the test results are not comparable.
(7) Flexible test and comprehensive analysis
Under normal circumstances, the cable line can be two-way fault test at both ends, and combined with the original data, calculate the location of the fault point. Then the test and calculation results of the two directions are analyzed and compared comprehensively, so that the specific location of the fault point can be judged more accurately. When there is no obvious feature on the route near the obstacle point and the specific obstacle point cannot be determined on site, the method such as measurement at the nearest junction or excavation at the obstacle point in the preliminary test can be adopted. The test instrument of the terminal station is in the real-time measurement state and can detect the curve change at any time, so as to find the accurate fault point of the optical fiber.
7 Cable fault judgment and handling should pay attention to matters
1. Matters needing attention when troubleshooting and repairing
(1) When the fault occurs at the provincial boundary or the junction of the two maintenance units, the two adjacent maintenance units should check and repair at the same time.
(2) All levels of optical cable line maintenance units should accurately grasp the information of their optical cable lines. Proficient in testing methods of cable line obstacle points, can accurately analyze and determine the location of obstacle points. Always maintain a certain strength of rush repair, and master the operation procedures of line rush repair and the use of rush dayong equipment.
(3) Optical cable maintenance personnel should be familiar with optical cable line information, proficient in line repair operation procedures, obstacle test methods and optical cable connection technology, strengthen the management of emergency repair vehicles, ready for emergency repair at any time.
Special equipment, tools, instruments, machinery and vehicles for emergency repair must be relatively concentrated, and a list should be made to make preparations at any time. Generally, loans and misappropriation are not allowed.
2. Matters needing attention in the process of processing
(1) In the process of emergency repair of optical cable lines, attention should be paid to the safety of the operation and use of instruments and equipment. Before the optical fiber fault test, the optical fiber under test is physically disconnected from the optical terminal machine at the opposite end.
(2) Once the fault is removed and passed the strict test, immediately notify the maintenance department to verify the transmission quality of the cable and resume communication as soon as possible.
(3) Carefully make fault check and repair records. After the fault is rectified, the line maintenance department shall organize related personnel to analyze the cause of the fault, sort out the technical data and report the fault according to relevant regulations. Summarize experience and lessons, and put forward improvement measures.
(4) Intervention or replacement of optical cable, should be used with the fault of the same manufacturer of the same type of optical cable, and as far as possible to reduce the cable connector and minimize the loss of optical fiber connection. The length of the cable involved or replaced in the process of troubleshooting should generally be not less than 200m, and the same manufacturer and model of cable should be used as far as possible. The average connector loss of single-mode fiber should not be greater than 0.2dB/ piece. The bending radius of the cable should not be less than 15 times the cable diameter after the fault is handled and the cable is changed.
3. Precautions should be taken when jumping fiber
(1) Before fiber hopping, test the spare fiber core first to ensure that the fiber core to be used meets relevant requirements.
(2) During troubleshooting, if you need to recover services through fiber hopping, obtain the consent of the transmission center in advance and keep in touch with the transmission room.
(3) It is strictly prohibited to remove and insert other in-use fiber cores that do not need fiber hopping, so as to avoid man-made failures.
(4) When removing and inserting the fiber core, remove and insert the fiber core one by one. After each core is removed, remove and insert the next core only after the transmission room confirms that it is normal.
(5) During fiber hopping, keep the fiber core clean, need to clean the head of fiber hopping, do not insert fiber hopping in a short time, should wear fiber hopping safety hat in time.
04-24
202404-23
202404-23
202404-08
202404-07
202403-26
202403-26
202403-18
202403-18
202403-13
2024