Communication optical cable is a common wiring product. You should choose according to the nature of the specific project. Today we will introduce the structure of communication optical cable.
Communication cable structure
cable core
Cable core: It is located in the center of the optical cable and is the main body of the optical cable; its function is to properly place the optical fiber so that the optical fiber can still maintain excellent transmission performance under certain external forces. Commonly used cable core structures are generally divided into the following four types:
1) Layer-twisted type, layer-twisted type is divided into two types: loose sleeve and tight sleeve.
2) Skeleton type, also known as trough type;
3) Belt type
4) Center beam tube type, usually referred to as beam tube type.
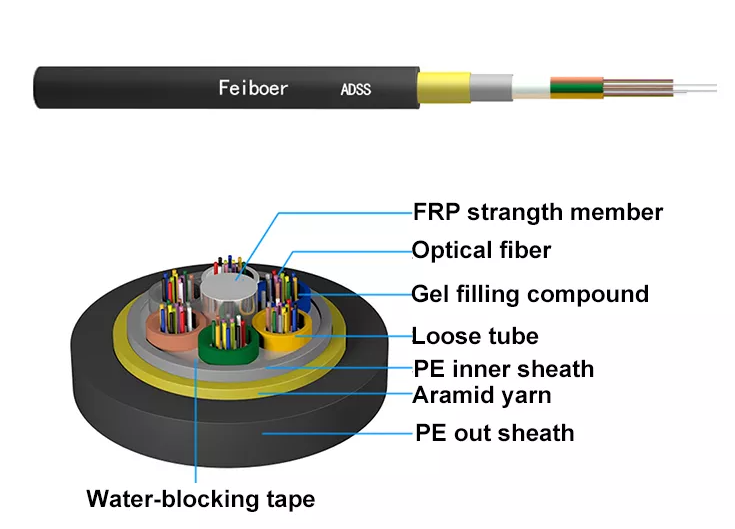
So, what is the difference in structure between optical cable and electric cable? Unlike cables, which inherently conduct metal and have a certain strength, optical cables must be provided with strengthening members to withstand mechanical tensile loads. Fiber optic cables have two ways of placing strength members:
1) The central strengthening core method placed in the middle of the cable core is often used in the layer stranding type and skeleton type. As shown in FIG. This strengthening method is mostly adopted in Europe and Japan.
2) The manner in which reinforcement members are placed on the outer periphery of the sheath. This method is mostly used in the United States.
Sheath
The sheath is located on the periphery of the cable core and consists of an inner sheath and an outer sheath.
1) Sheath
The sheath commonly used for optical cables is a semi-hermetic bonded sheath. It consists of double-sided plastic-coated aluminum strips (PAP) or steel strips (PSP) longitudinally bonded outside the cable core. In addition to providing mechanical protection for the cable core, the sheath mainly prevents moisture or water from entering the cable core. Optical cables with PAP sheaths can be laid directly in ducts or overhead. The optical cable with PSP sheath can be used for direct burial laying. Of course, there are better fully sealed metal sheaths, but the production cost is higher.
2) Outer sheath
The outer sheath (outer jacket) provides further protection to the cable jacket. It's like putting "armor" on the optical cable, we call it armor. Usually in direct burial, climbing, underwater, anti-rat and other occasions, it is necessary to armor the optical cable. The types of armor include plastic-coated steel tape, stainless steel tape, single-layer steel wire, double-layer steel wire, etc., and sometimes nylon armor is used. In addition to the armor layer, it is necessary to add an outer layer to prevent the metal armor from being corroded.
In order to prevent the moisture from spreading around once it enters the interior of the cable, most cables are filled with a compound (ointment) in the cable core, which is called an oil-filled cable. It has the advantages of low investment and small maintenance workload.
Of course, there are also inflatable optical cables, using the inflatable maintenance method we introduced earlier, so that real-time monitoring can be realized, and it has the advantage of timely troubleshooting. The disadvantage is that the cost is higher.
04-24
202404-23
202404-23
202404-08
202404-07
202403-26
202403-26
202403-18
202403-18
202403-13
2024